
Make sure children ages 12 and younger are always properly buckled in the back seat in a car seat, booster seat, or seat belt—whichever is appropriate for their age, weight, and height.
Data show:
• Booster Seats reduce the risk for serious injury by 45% for children ages 4–8, compared with seat belt use alone.
• Car Seats use reduce the risk for injury in crashes by 71–82% for children, compared with seat belt use alone.
• Seat Belts reduce the risk for death and serious injury by about half for older children and adults.
Source: Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC)
According to the Washington Traffic Safety Commission, car crashes are a leading killer of children ages 1-13. Using the right seat can reduce the risk of fatal injury by 71%.
Washington’s Child Restraint Law (RCW 46.61.687) helps ensure you are correctly using the right seat for your child’s age and size.
Follow these requirements to GREATLY REDUCE chance of death or serious injury:
In Washington State, you can get a traffic ticket if your child is not properly restrained.
Children under age 2 must be properly secured in a rear-facing car seat.
Children ages 2-4 must be properly secured in a car seat with a rear or forward facing harness.
Children 4 or older and less than 4’9″ tall must be secured in a booster seat with seat belt (or) continue in harness seat.
Children over height 4’9″ (typically starting at 8-12 years old) must be secured by a properly fitted seat belt.
Children under age 13 are required to ride in the back seat when practical to do so.
Every child restraint system must comply with U.S. Department of Transportation standards (and) be used according to vehicle (and) child restraint manufacturer.
For the safest protection, a child should remain in each stage of the restraints until they reach the maximum height (and) weight based on the manufacturer’s instructions.
Source: Washington Traffic Safety Commission (WA Child Safety Program). Requirements effective 1/1/2020.
To learn more about Washington ’s Child Restraint Law, visit wacarseats.com >>
Laws regarding child safety restraints vary by state. The Governors Highway Safety Association (GHSA) offers a state-by-state overview of restraint laws.
For a state-by-state overview of child safety restraints, visit ghsa.org >>
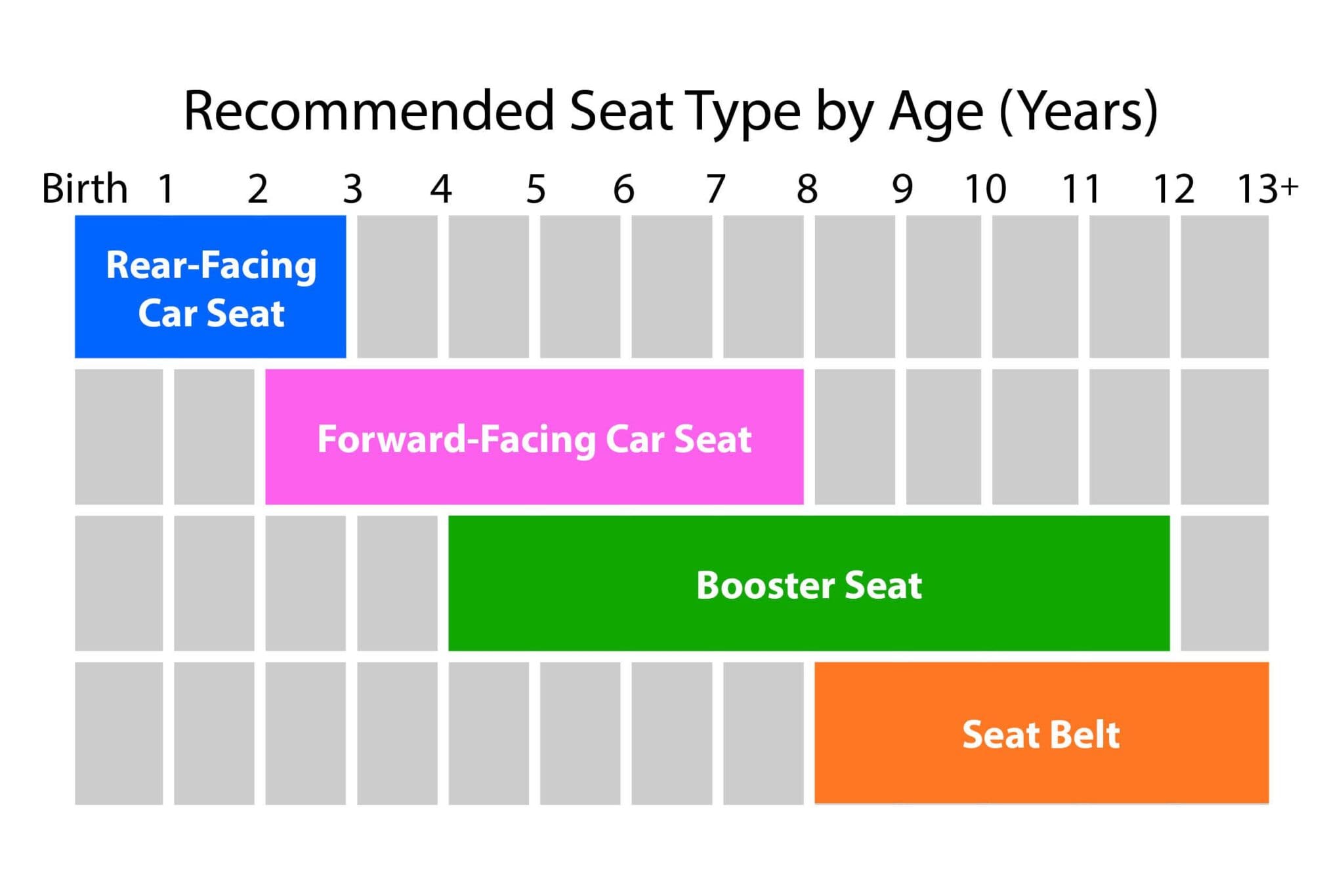
For the safety of your child, it’ s important not to rush from one seat type to the next.
Child Restraint Safety seat types include:
Rear-facing Only Seats usually fit 29-32 inches and 4-30 lbs. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines.
• Children should be in rear-facing seats through at least age 2 and until they reach the manufacturer’s maximum recommended weight and height.
• It is fine if your baby’s feet touch the back of the vehicle seat, or their legs naturally bend while in the car seat.
• Pros: Portable, attaches to strollers, lifts out of base in the car.
• Cons: Must be replaced with a forward-facing car seat once your baby reaches the upper limit on weight or height.

Convertible Car Seats usually fit up to 52 in. and 5-65 lbs. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines.
• Works as either a rear-facing or forward-facing car seat, based on the child’s size.
• Keep children in the rear-facing position until at least age 2; use the rear-facing position as long as possible until reaching the maximum height or weight in the manufacturer guidelines.
• Children’s legs may bend naturally against the back of the vehicle seat when they are in a rear-facing position. This is fine as long as the child is still within the manufacturer’s height guidelines.
• Pros: Can be used longer with a greater range of weight and height, as the rear-facing seat “converts” to a forward-facing seat as the child grows.
• Cons: Takes up more room, cannot attach to stroller.

Forward-facing Car Seats usually fit over 20 lbs., minimum 2 years of age. You may be able to convert to a booster seat when your child is tall enough or weighs enough. Always check the manufacturer’s guidelines.
• Children should be kept in rear-facing car seats as long as possible (until they reach the manufacturer’s maximum recommended height or weight).

Booster Seats usually fit children who have outgrown forward-facing car seats but do not yet fit adult seat belts (minimum 40 lbs.).
• High-back booster seats can be used in vehicles with or without headrests.
• No-back booster seats can generally be used where your vehicle has a headrest that fits the child comfortably.
Your owner’s manual will help determine the best option for the age and size of your child, and the specifics of your vehicle.
• Lap belt fits low across the hip bones, touching the top of the thighs.
• Shoulder belt fits across the center of the shoulder. When the child leans forward and back, the belt should unspool easily and retract without leaving slack.

Seat Belts should be worn by themselves only when they fit your child correctly, which can vary by vehicle.
A properly fitted seat belt:
• Ensures your car’s other safety features are as effective as possible during a crash.
• Has a lap belt that sits low across the hip bones, not on the abdomen.
• Has a shoulder belt that lies across the center of the shoulder and chest, not rubbing against the neck or tucked behind the arm.
• Fits your child when they sit all the way back in the vehicle seat with their knees bent comfortably.
• Can be worn properly through the entire ride.
• Is used every trip, every time, by everyone in the car. You set the example!


For more information, visit the Ultimate Car Seat Guide to learn more about transitioning your child into a Seat Belt >>
Booster Seats and Car Seats keep your child in place so that all of your vehicle’s safety features can work correctly during a crash. Until your child is taller than 4′ 9″ (generally 8-12 years old), your vehicle’s seat belt will not fit correctly.
Follow these important steps to:
For more information, visit theNational Highway Traffic Safety Administration >>

Car Seats & Booster Seats allow your vehicle’s safety features to be as effective as possible.
Watch this video of a crash test demonstrating how a lap belt alone isn’t enough protection for a 6-year-old child.
Watch this video playlist from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) including instructions for installing various types of Booster Seats and Car Seats.
Directions: In YouTube, use the top right corner menu to browse Seat Types.
Courtesy: National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
When installing a booster seat, follow the owners’ manual for your booster seat as well as your vehicle regarding “child restraint systems.” These guidelines will provide instructions on seat placement and angle.
Booster seats must be used with a lap and shoulder belt, not a lap belt alone.
In the Seattle area, Seattle Children’s Hospital regularly offers FREE Car Seat Checks to ensure proper installation and fit. Specific car seats vary, but the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) offers Car Seat Installation Instructions.
Booster seats must be used with a lap and shoulder belt together.
If the center of your back seat has a lap-only belt, place the booster seat in an outboard seat that has a lap and shoulder belt.
If you do not have a usable lap and shoulder belt in the back, you can use the booster in the front seat with the lap and shoulder belt. Push the front seat back as far as you can. If your car has an air bag, turn it off.
If you must use a lap-only belt, your child should wear it low and tight across the hips without using a booster seat.
No-back Booster Seats can be used in cars with headrests in the back seat. If your child’s head does not rest comfortably in the headrest, use a high-back booster seat.
High-back Booster Seats can be used in cars with or without headrests.
Source: Seattle Children’s Hospital and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
Share these FREE Resources to ensure that Car Seats and Booster Seats are installed safely and correctly >>
Seattle Children’s Hospital
• Car Safety
• Aftermarket Car Seat Products
• Booster Seats
• Car Seat Checks
• Car Seat Safety
Safe Kids Worldwide
• Car Seat Checkups and Educational Workshops
• Participate in a Seat Study
• Visit a Seat Inspection Station
• Share Seat Safety Tips
• Register your Seat
• Check for Recalls
Booster Seats and Car Seats may be recalled due to documented mechanical problems, mislabeling that can lead to confusion, incorrect user instructions or other safety concerns.
What Can I Do?
• Register your Booster Seat or Car Seat with the manufacturer to receive important notifications about your product.
• Check for recalls and register to receive recall notifications.
Seattle Children’s
• Car Seat Safety Guidelines (Information available in English and Spanish)
• Booster Seats (Information available in English, Spanish, Amharic, Chinese, Oromo, Somali, Vietnamese)
Public Health – Seattle & King County
• Car seats, booster seats and seatbelts
Safe Kids Washington
• Car Seat Checks, Events and Educational Workshops
American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP)
• Child Passenger Safety
• Car Seats: Information for Families
National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA)
• Car Seats & Booster Seats
• Car Seat Glossary
• Training Contacts by State for Child Passenger Safety
• Car Seat Use After a Crash
• Keeping Kids Safe – A parent’s guide to protecting children in and around cars
• Used Car Seat Safety Checklist
Federal Aviation Administration (FAA)
For more resources, visit hiprc.org >>
This website is provided for educational and informational purposes only and does not constitute providing medical advice or professional services. The information provided should not be used for diagnosing or treating a health problem or disease, and those seeking personal medical advice should consult with a licensed physician. No physician-patient relationship is created by this web site or its use. Neither HIPRC, the University of Washington, nor its employees, nor any contributor to this website, makes any representations, express or implied, with respect to the information provided herein or to its use.